Create a webhook automation
9 minute read
This page shows how to create a webhook automation. To create a Slack automation, refer to Create a Slack automation instead.
At a high level, to create a webhook automation, you take these steps:
- If necessary, create a W&B secret for each sensitive string required by the automation, such as an access token, password, or SSH key. Secrets are defined in your team settings.
- Add a webhook integration to define the webhook’s endpoint and authorization details and grant the integration access to any secrets it needs.
- Create the webhook automation to define the event to watch for and the payload W&B will send. Grant the automation access to any secrets it needs for the payload.
Add a webhook integration
A team admin can add a webhook integrations to the team.
-
Log in to W&B and go to Team Settings page.
-
In the Webhooks section, click New webhook.
-
Provide a name for the webhook.
-
Provide the endpoint URL for the webhook.
-
If the webhook requires an access token or any other secrets for authentication, grant the webhook access to each secret by setting Secret to the secret’s name. When you configure the automation that uses the webhook, you can access the secret as a payload variable by prefixing its name with
$.If the webhook’s access token is stored in a secret, you must also complete the next step to specify the secret as the access token.
-
If required, set Access token to the name of the secret that contains the token. When you configure an automation that uses the webhook, you can access the token in the
${ACCESS_TOKEN}payload variable, and the HTTP header setsAuthorization: Bearerto the access token. Your webhook’s authentication and authorization requirements are determined by the webhook’s service. -
Click Test. W&B attempts to authenticate to the webhook’s endpoint using the accesss token you configured.
Optionally, provide a payload to test. To refer to a secret the webhook has access to in the payload, prefix its name with
$. This payload is only used for testing and is not saved. You configure an automation’s payload when you create the automation. See Troubleshoot your webhook to view where the secret and access token are specified in the POST request.
Now you can create a webhook automation.
Create a webhook automation
After you configure a webhook integration, select Registry or Project, then follow these steps to create a webhook automation.
A Registry admin can create automations in that registry. Registry automations are applied to all collections in the registry, including those added in the future.
-
Log in to W&B.
-
Click the name of a registry to view its details,
-
To create an automation that applies to the registry and all of its collections (including those created in the future), click the Automations tab, then click Create automation.
To create an automation that applies only to a specific collection, click the collection’s action
...menu, then click Create automation. Alternatively, create an automation for a collection from the Automations section of the collection’s details page by clicking Create automation. -
Choose the Event to watch for.
- Fill in any additional fields that appear, which depend upon the event. For example, if you select An artifact alias is added, you must specify the Alias regex.
Click Next step.
-
Select the team that owns the webhook integration.
-
Set Action type to Webhooks. then select the webhook integration to use.
-
If your webhook requires a payload, construct it and paste it into the Payload field. Refer to Payload variables. Your webhook’s requirements are determined by the webhook’s service.
-
Click Next step.
-
Provide a name for the automation. Optionally, provide a description. Click Create automation.
A W&B admin can create automations in a project.
-
Log in to W&B and go to the project page.
-
In the sidebar, click Automations.
-
Click Create automation.
-
Choose the Event to watch for.
-
Fill in any additional fields that appear, which depend upon the event. For example, if you select An artifact alias is added, you must specify the Alias regex.
-
Optionally specify a collection filter. Otherwise, the automation is applied to all collections in the project, including those added in the future.
Click Next step.
-
-
Select the team that owns the webhook integration.
-
Set Action type to Webhooks. then select the webhook integration to use.
-
If your webhook requires a payload, construct it and paste it into the Payload field. Refer to Payload variables. Your webhook’s requirements are determined by the webhook’s service.
-
Click Next step.
-
Provide a name for the automation. Optionally, provide a description. Click Create automation.
View and manage automations
- Manage the registry’s automations from the registry’s Automations tab.
- Manage a collection’s automations from the Automations section of the collection’s details page.
From either of these pages, a Registry admin can manage existing automations:
- To view an automation’s details, click its name.
- To edit an automation, click its action
...menu, then click Edit automation. - To delete an automation, click its action
...menu, then click Delete automation. Confiruation is required.
A W&B admin can view and manage a project’s automations from the project’s Automations tab.
- To view an automation’s details, click its name.
- To edit an automation, click its action
...menu, then click Edit automation. - To delete an automation, click its action
...menu, then click Delete automation. Confiruation is required.
Payload reference
Use these sections to construct your webhoook’s payload. For details about testing your webhook and its payload, refer to Troubleshoot your webhook.
Payload variables
This section describes the variables you can use to construct your webhook’s payload.
| Variable | Details |
|---|---|
${project_name} |
The name of the project that owns the mutation that triggered the action. |
${entity_name} |
The name of the entity or team that owns the mutation that triggered the action. |
${event_type} |
The type of event that triggered the action. |
${event_author} |
The user that triggered the action. |
${artifact_collection_name} |
The name of the artifact collection that the artifact version is linked to. |
${artifact_metadata.<KEY>} |
The value of an arbitrary top-level metadata key from the artifact version that triggered the action. Replace <KEY> with the name of a top-level metadata key. Only top-level metadata keys are available in the webhook’s payload. |
${artifact_version} |
The Wandb.Artifact representation of the artifact version that triggered the action. |
${artifact_version_string} |
The string representation of the artifact version that triggered the action. |
${ACCESS_TOKEN} |
The value of the access token configured in the webhook integration, if an access token is configured. The access token is automatically passed in the Authorization: Bearer HTTP header. |
${<SECRET>} |
If configured, the value of a secret configured in the webhook integration. Replace <SECRET> with the name of the secret. |
Payload examples
This section includes examples of webhook payloads for some common use cases. The examples demonstrate how to use payload variables.
Send a repository dispatch from W&B to trigger a GitHub action. For example, suppose you have workflow that accepts a repository dispatch as a trigger for the on key:
on:
repository_dispatch:
types: BUILD_AND_DEPLOY
The payload for the repository might look something like:
{
"event_type": "BUILD_AND_DEPLOY",
"client_payload":
{
"event_author": "${event_author}",
"artifact_version": "${artifact_version}",
"artifact_version_string": "${artifact_version_string}",
"artifact_collection_name": "${artifact_collection_name}",
"project_name": "${project_name}",
"entity_name": "${entity_name}"
}
}
event_type key in the webhook payload must match the types field in the GitHub workflow YAML file.The contents and positioning of rendered template strings depends on the event or model version the automation is configured for. ${event_type} will render as either LINK_ARTIFACT or ADD_ARTIFACT_ALIAS. See below for an example mapping:
${event_type} --> "LINK_ARTIFACT" or "ADD_ARTIFACT_ALIAS"
${event_author} --> "<wandb-user>"
${artifact_version} --> "wandb-artifact://_id/QXJ0aWZhY3Q6NTE3ODg5ODg3""
${artifact_version_string} --> "<entity>/model-registry/<registered_model_name>:<alias>"
${artifact_collection_name} --> "<registered_model_name>"
${project_name} --> "model-registry"
${entity_name} --> "<entity>"
Use template strings to dynamically pass context from W&B to GitHub Actions and other tools. If those tools can call Python scripts, they can consume the registered model artifacts through the W&B API.
-
For more information about repository dispatch, see the official documentation on the GitHub Marketplace.
-
Watch the videos Webhook Automations for Model Evaluation and Webhook Automations for Model Deployment, which guide you to create automations for model evaluation and deployment.
-
Review a W&B report, which illustrates how to use a Github Actions webhook automation for Model CI. Check out this GitHub repository to learn how to create model CI with a Modal Labs webhook.
Configure an ‘Incoming Webhook’ to get the webhook URL for your Teams Channel by configuring. The following is an example payload:
{
"@type": "MessageCard",
"@context": "http://schema.org/extensions",
"summary": "New Notification",
"sections": [
{
"activityTitle": "Notification from WANDB",
"text": "This is an example message sent via Teams webhook.",
"facts": [
{
"name": "Author",
"value": "${event_author}"
},
{
"name": "Event Type",
"value": "${event_type}"
}
],
"markdown": true
}
]
}
You can use template strings to inject W&B data into your payload at the time of execution (as shown in the Teams example above).
Set up your Slack app and add an incoming webhook integration with the instructions highlighted in the Slack API documentation. Ensure that you have the secret specified under Bot User OAuth Token as your W&B webhook’s access token.
The following is an example payload:
{
"text": "New alert from WANDB!",
"blocks": [
{
"type": "section",
"text": {
"type": "mrkdwn",
"text": "Registry event: ${event_type}"
}
},
{
"type":"section",
"text": {
"type": "mrkdwn",
"text": "New version: ${artifact_version_string}"
}
},
{
"type": "divider"
},
{
"type": "section",
"text": {
"type": "mrkdwn",
"text": "Author: ${event_author}"
}
}
]
}
Troubleshoot your webhook
Interactively troubleshoot your webhook with the W&B App UI or programmatically with a Bash script. You can troubleshoot a webhook when you create a new webhook or edit an existing webhook.
A team admin can test a webhook interactively with the W&B App UI.
- Navigate to your W&B Team Settings page.
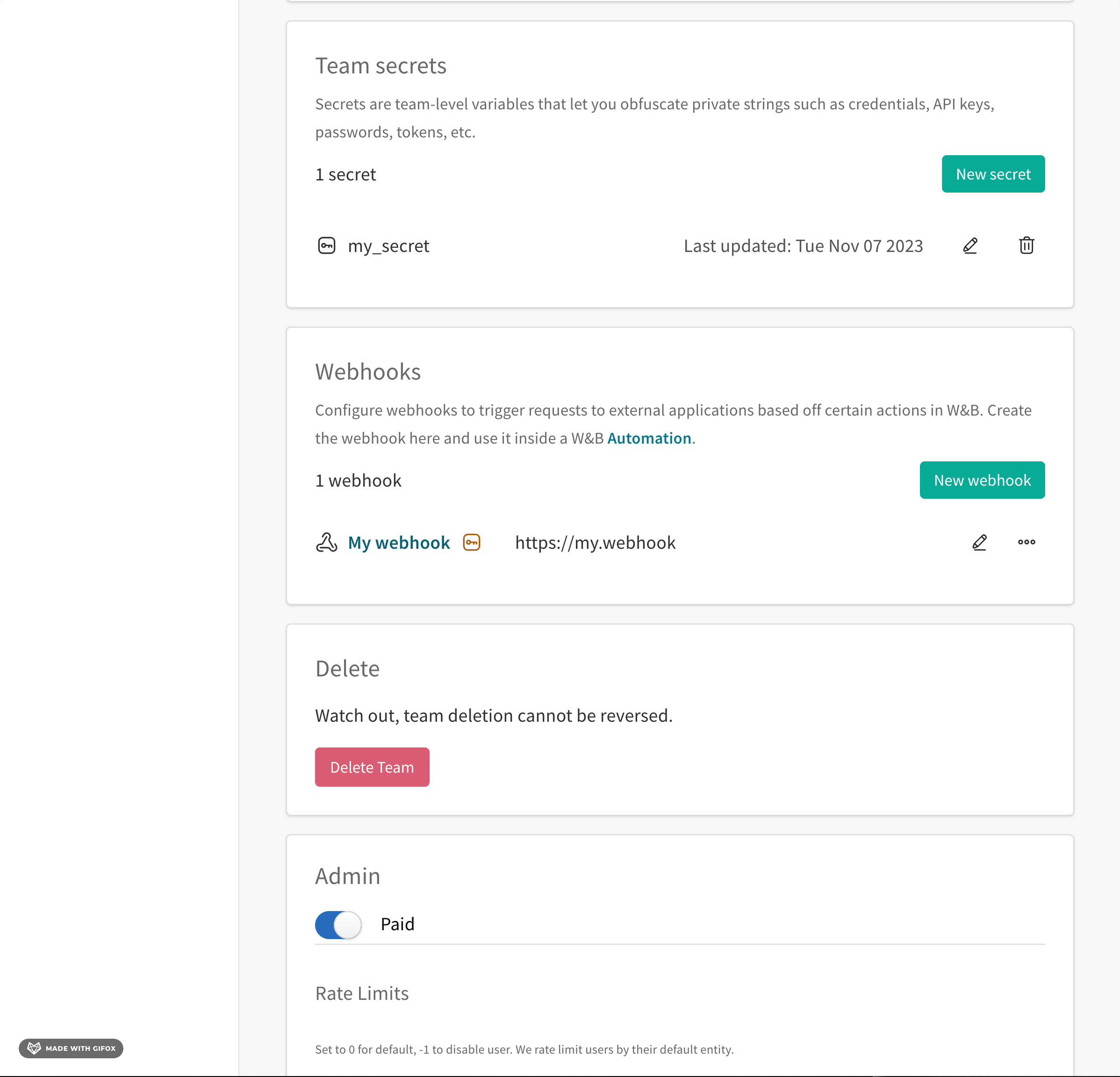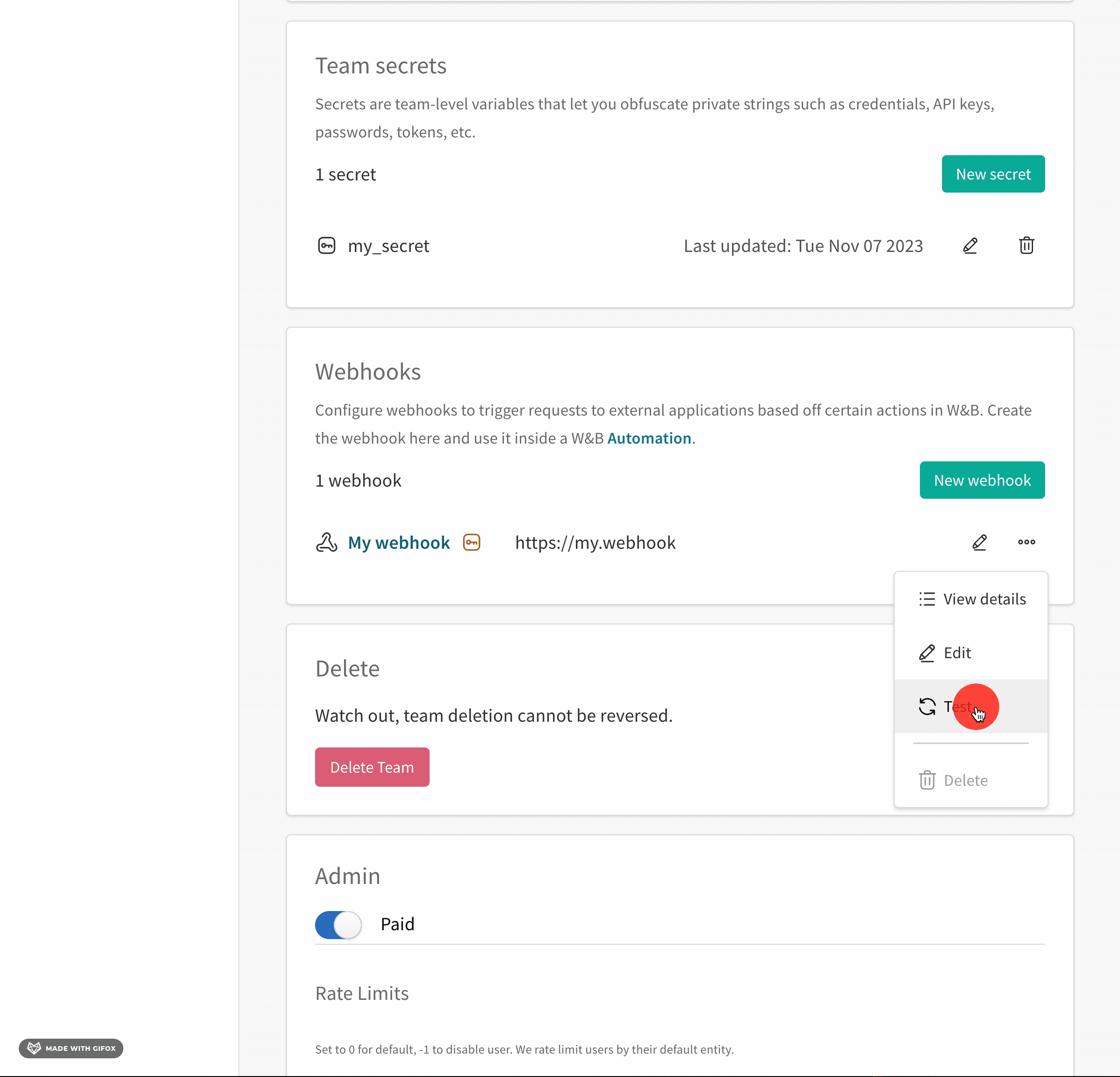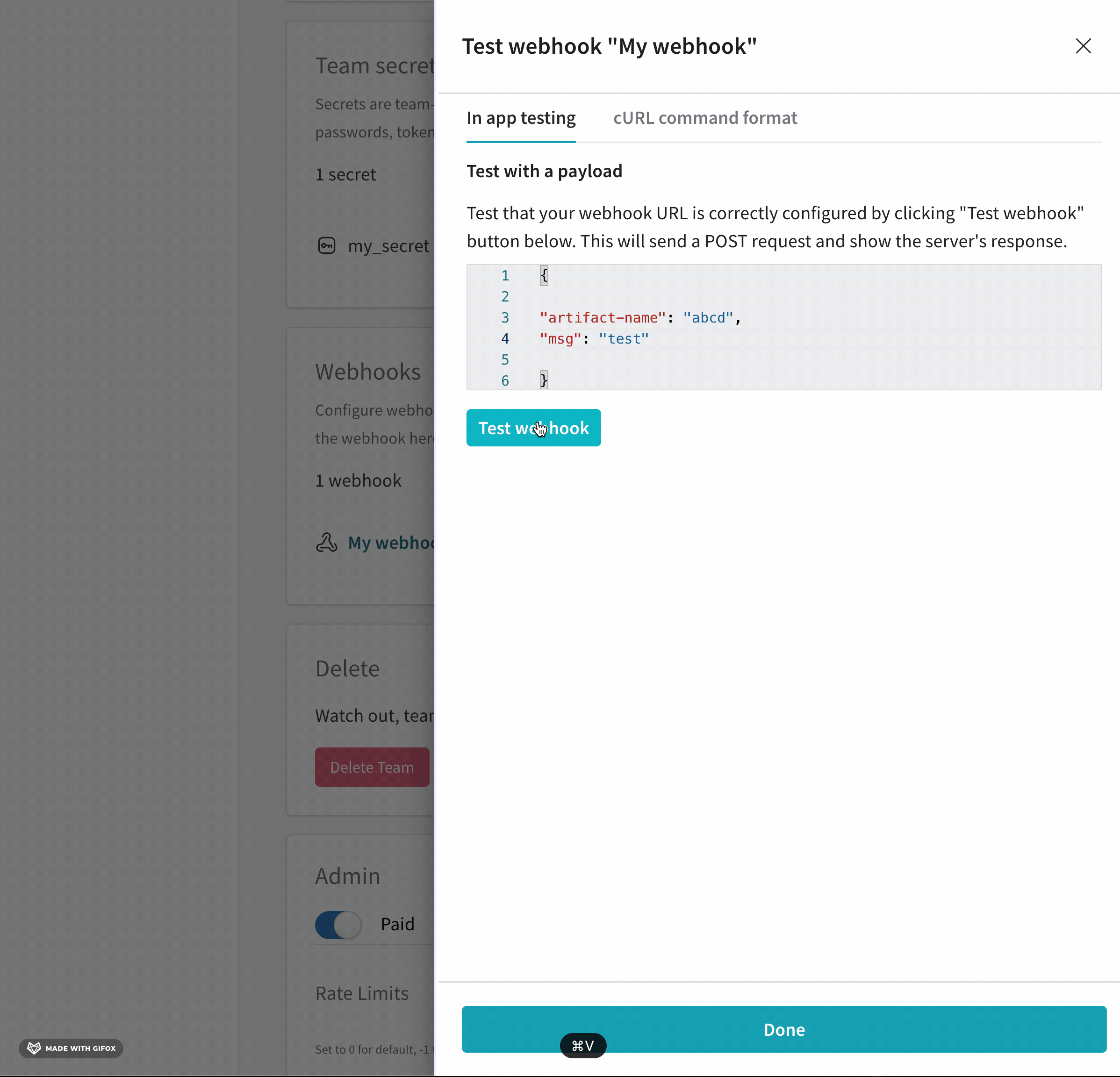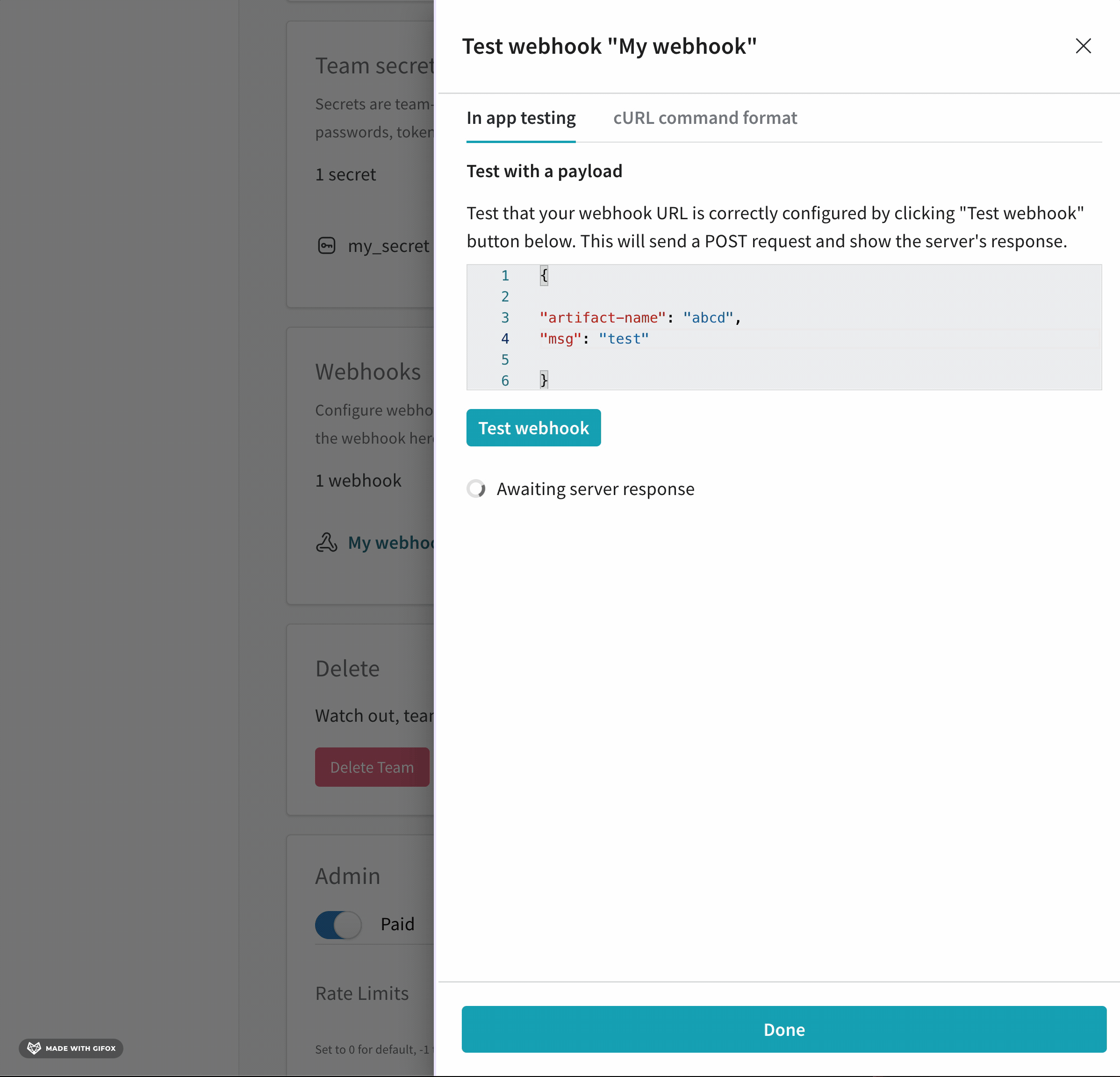
- Scroll to the Webhooks section.
- Click on the horizontal three docs (meatball icon) next to the name of your webhook.
- Select Test.
- From the UI panel that appears, paste your POST request to the field that appears.
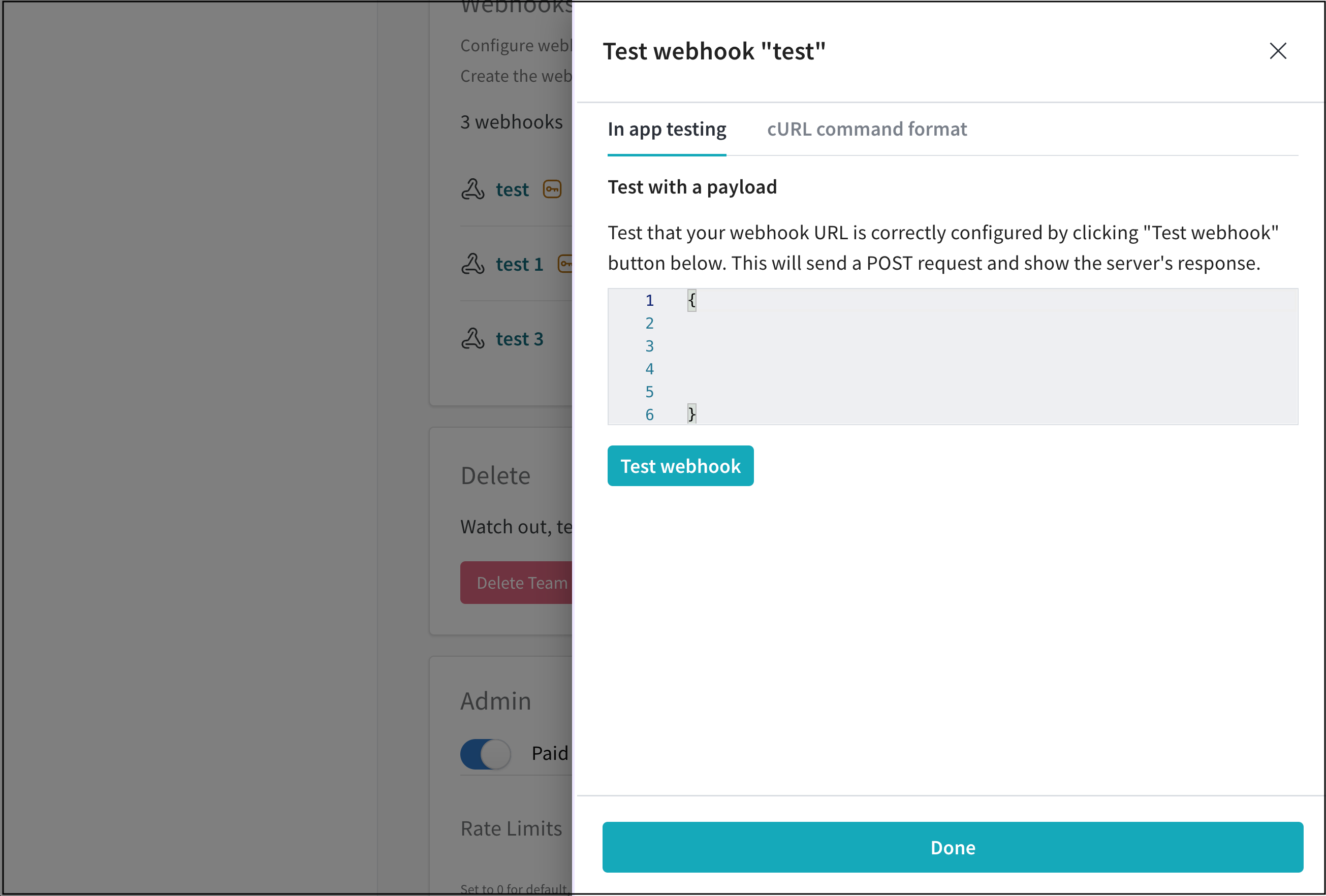
- Click on Test webhook. Within the W&B App UI, W&B posts the response from your endpoint.
Watch the video Testing Webhooks in Weights & Biases for a demonstration.
This shell script shows one method to generate a POST request similar to the request W&B sends to your webhook automation when it is triggered.
Copy and paste the code below into a shell script to troubleshoot your webhook. Specify your own values for:
ACCESS_TOKENSECRETPAYLOADAPI_ENDPOINT
webhook_test.shFeedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.